Basal cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins with a pimple
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the basal cells and appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the basal cells (a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off). This condition often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, but it can also take other forms.
Notably, Basal cell carcinoma mostly occurs in the areas of skin that are exposed to the sun, such as on the head and neck.
Most basal cell cancer can be the result of long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, claims reports. This is why one shouldn’t avoid using sunscreen, as it may help protect against this condition.
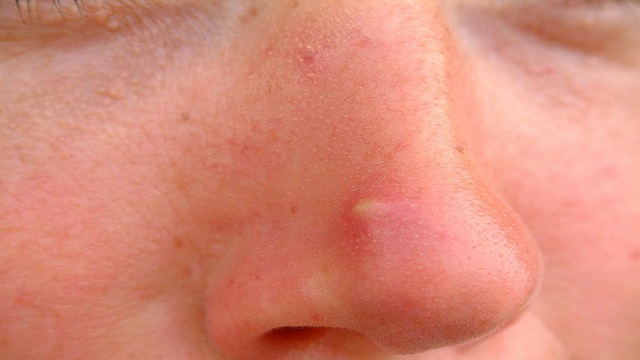
Michelle Davis who suffered Basal cell carcinoma
Recently, a 52-year-old woman named Michelle Davis, who noticed a hard pimple on her nose, discovered that the seemingly harmless cyst was actually skin cancer. She first noticed the red pimple in April 2022 and thought it was a usual spot and would cover it up with concealer while going to work every day.
“It was really hard. Like a volcano under the skin,” the New Zealand-based account manager said, “I went walking with my girlfriend and it went purple and she pointed it out. I said, ‘It’s just a pimple’.”
By January 2023, the spot became “really sore” and Davis tried to pop it. However, “Nothing happened. Then it bled and bled. I thought ‘That’s not normal’,” she said.
It was then that the 52-year-old contacted a doctor and the expert immediately thought it was cancer. Following this, a biopsy was conducted and it was confirmed that she had basal cell carcinoma- a common form of non-melanoma skin cancer.
“I was in shock when I found out,” said Michelle and added, “I had never heard of basal cell carcinoma.” The elderly woman underwent a nasal flap reconstruction in April this year to remove the cancer.
“They cut up my nose in a zig-zag. They cut out a crater. There was a hole at the end of my nose. They then bring the skin down to cover it,” Michelle explained. The surgery left a scar on her nose along with asymmetrical nostrils.
Symptoms
As mentioned earlier, Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on sun-exposed parts of your body. Very rarely can they develop on parts of your body usually protected from the sun, genitals for example.
This condition often appears as a change in the skin and grows into a sore that won’t heal. Some basic symptoms of Basal cell carcinoma:
- A shiny, skin-coloured bump: Basal cell cancer appears as a translucent yet shiny bump, meaning it can be seen only a tiny bit through the surface. The bump can look pearly white or pink on white skin. Meanwhile, on brown and black coloured skin, the bump often looks brown or glossy black. Tiny blood vessels might also be visible, though they might be difficult to see on darker skin. The bump may bleed and scab over.
- Lesion: A brown, blue, or black lesion- dark spot- may appear on the bump along with a slightly raised, translucent border.
- A flat, scaly patch: A flat, scaly patch with a raised edge is one of the looks it possesses. These patches can grow quite large over time.
- A white, waxy, scar-like lesion without a clearly defined border.
Causes
When one of the skin’s basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA, it turns into carcinoma/cancer. Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis- the outermost layer of skin- and they are responsible for the production of new cells. When new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin’s surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off.
The process of creating new skin cells is controlled by a basal cell’s DNA. The DNA carries instructions that command cells and put them into their right work position. The mutation allows the basal cells to multiply rapidly and continue growing when until it dies naturally. Eventually, the accumulating abnormal cells may form a cancerous tumor — the lesion that appears on the skin.
Another huge factor responsible for the mutation of basal cells is thought to be ultraviolet (UV) radiation found in sunlight and in commercial tanning lamps and tanning beds. But, sun exposure is rarely the reason for skin cancers that develop on skin not exposed to direct sunlight.
Prevention
- Avoid the sun during the middle of the day
- Wear sunscreen every day
- Wear protective clothing
- Avoid tanning beds
- Check your skin regularly and report changes to your doctor.
Meanwhile, if at any point you see something unusual or anything closer to the symptoms of basal cell carcinoma, make an immediate appointment with your dermatologist.



 Ms Kalinga
Ms Kalinga